Minoxidil (Rogaine) Sexual Side-Effects: All You Need To Know
Minoxidil is a popular and effective hair-loss medication. It helps reduce hair shedding while stimulating hair regrowth! However, like any drug, minoxidil can have some side effects. Some even speculated on the impact of minoxidil on sexual health.
In this article, we’ll explore minoxidil’s (Rogaine) side effects sexually. We’ll also provide alternatives to this hair-loss drug. So, stick around!
How Does Minoxidil Work?
Before jumping right into minoxidil’s sexual side effects, let’s discuss how this drug works. As you might know, minoxidil, commercially known as Rogaine, is an over-the-counter medication for hair loss.
Typically, the drug is used to treat patients with androgenetic alopecia (male-pattern baldness) and female-pattern hair loss. However, it was originally a medication for high blood pressure.
Now, you might wonder: how does minoxidil help improve hair loss symptoms?
The exact mechanism of Rogaine isn’t yet fully understood. However, minoxidil lowers blood pressure and promotes hair regrowth mainly through its hyperpolarization action.
Aside from that, minoxidil might work as an antiandrogen. That means it helps block male sex hormones’ action.
Here’s a detailed explanation of each mechanism:
Hyperpolarization of the Cell Membrane
Minoxidil is a potassium channel opener, a trait that allows it to change the charges around the cell membrane. As a result, the cell becomes more negative, a process known as hyperpolarization.
You see, cells have a gateway structure known as ion channels. Those cell membrane proteins regulate both the entry and exit of essential nutrients and water.
Now, what happens when you apply topical minoxidil to your scalp? The hair growth drug causes the potassium gateways to open. That results in the efflux of positive potassium ions. Consequently, the cell membrane becomes more negative.
Such a process increases the flow of oxygen, blood, and nutrients to the hair follicles. As you might have guessed, that stimulates hair growth, increasing its density and length.
Antiandrogen Effects
Although the main action of minoxidil is to increase blood flow to the hair, studies show this chemical can have antiandrogen effects.
However, the drug doesn’t directly block the action of male sex hormones. Instead, minoxidil downregulates the 5-alpha reductase enzyme.
The former converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is the root cause of male pattern baldness as it shrinks the hair follicle and affects the hair cycle.
Using Rogaine can stop the genes that regulate 5-alpha reductase production, potentially reducing DHT levels. Still, further research is needed to determine the antiandrogenic effects of minoxidil, as it’s not marketed as a DHT blocker.
Minoxidil Side Effects Sexually
From the above, you can see that minoxidil’s mode of action has little connection with male sex hormones, unlike finasteride. The latter is a DHT blocker used to treat male pattern baldness. Although effective, finasteride poses several side effects that cause sexual issues.
However, a 2016 review submitted to the FDA’s Adverse Event Reporting System (FARES) reported some sexual side effects from minoxidil users. Those include:
Erectile Dysfunction
As the name implies, erectile dysfunction is the difficulty of getting or keeping an erection. Typically, the former condition is common in middle-aged and older males between the ages of 40 and 70.
Several reasons can cause erectile dysfunction (ED). Those include:
- Vascular disease: Problems with the blood vessels can cause low blood supply to the penis, which can result in ED.
- Psychological disorders: This includes depression, stress, and performance anxiety.
- Neurological disorders: Sleep disorders and nerve damage due to diseases like multiple sclerosis can also cause ED.
- Physical and hormonal problems: These include obesity, diabetes, and low testosterone, among other causes.
Does Minoxidil Cause ED?
There isn’t much scientific data that links minoxidil with erectile dysfunction. However, only four male alopecia patients using minoxidil reported having ED in the 2016 FARES report.
Plus, according to the National Library of Medicine, erectile dysfunction isn’t recognized as one of minoxidil’s adverse effects. So, the chances of this OTC drug causing ED are slim to none.
It’s worth mentioning, however, that some doctors prescribe minoxidil in combination with finasteride.
Additionally, some products add DHT blockers, like azelaic acid, to topical minoxidil. In that case, your chances of having erectile dysfunction increase since DHT helps prevent erectile failure.
Low Libido
Libido is a term that’s used to describe the sexual drive. Low libido refers to a decrease in sexual desire, whether temporary or long-term. The former condition affects both men and women.
Several biological and psychological factors contribute to low libido. The former include low sex hormone levels as well as neurotransmitters, such as dopamine.
As for the latter, it includes relationship issues, stress, aging, and mental health conditions. Generally, there’s no such thing as a normal sexual drive; it varies from person to person. Still, a decrease in libido can cause distress.
Now, there are no scientific studies covering the relationship between low libido and minoxidil.
However, in the 2016 FARES study, two male alopecia patients using minoxidil reported experiencing sexual dysfunction. One case had decreased libido, while the other had a complete loss of sexual drive.
As you can see, such statistics are insignificant, which indicates that using minoxidil most likely won’t affect libido.
Ejaculation Disorder
Another common male sexual problem is ejaculation disorders, such as premature, delayed, retrograde, and anejaculation ejaculation. All ejaculation disorders can make it difficult to conceive a baby.
In some cases, such disorders can cause infertility. For instance, retrograde ejaculation is a condition where semen enters the bladder instead of exiting through the penis. That leads to low or no sperm, reducing the chances of egg fertilization.
Similarly, anejaculation is the inability to ejaculate semen, causing infertility. Several biological and physiological factors can cause those unpleasant disorders. Drugs, like antidepressants and high blood pressure medications, can also cause ejaculation problems.
Still, Rogaine doesn’t pose such adverse effects. According to the 2016 review, only one androgenetic alopecia patient reported having ejaculation problems when using minoxidil to treat hair loss.
Decreased Seminal Volume
As the name implies, decreased seminal volume, or hypospermia, occurs when the ejaculated semen volume is less than 2 mL. Such a problem is common for older men and is related to weak ejaculation.
Low androgen hormone levels, weak pelvic muscles, and ejaculation disorders are some of the factors that cause decreased seminal volume.
Now, studies show that minoxidil doesn’t directly affect male sex hormones. However, it might suppress androgen receptor-related functions. Consequently, it influences the function of androgen hormones.
While such action can potentially cause sexual side effects, only one case in the 2016 report had decreased seminal volume after using minoxidil. Until further research proves otherwise, Rogaine is less likely to cause weak ejaculation.
Does Minoxidil Affect Hormones?
As mentioned earlier, minoxidil doesn’t directly affect male hormones; it doesn’t reduce DHT or testosterone levels, unlike finasteride.
However, a 2014 study found that Rogaine can block the function of androgen receptors. For those who don’t know, each hormone binds to specific cell receptors, forming a complex. This process activates the hormone’s function.
Minoxidil suppresses the genes responsible for forming androgen receptors (AR). Additionally, it decreases AR stability. As a result, it interferes with androgen receptors’ activity.
That said, further research is needed to know if minoxidil’s effect on androgen receptors influences the function of male sex hormones.
Common Minoxidil Side Effects
While sexual dysfunction isn’t known as an adverse effect of minoxidil, the hair loss treatment can still cause other side effects. Those include:
- Scalp itching
- Skin irritation
- Local acne breakouts
- Rashes
- Redness and swelling
- Facial hair growth
- Heartbeat problems
- Dizziness and fainting
If you experience any of the above or similar symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Minoxidil Alternatives to Limit Sexual Problems
Here are some minoxidil alternatives for those who are allergic to the drug or want a product with fewer side effects:
Hair Transplant
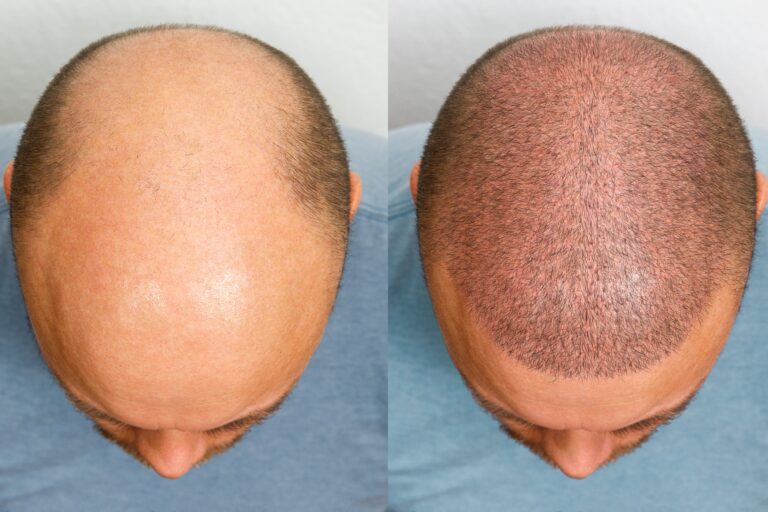
Sure, hair transplants, like FUT and FUE, aren’t OTC medications. However, those treatments are generally more effective than minoxidil and finasteride. That’s because the latter won’t stimulate dead follicles to grow hair.
In contrast, during hair transplants, the surgeon implants hair to cover up balding spots, replacing dead follicles with active ones. Not to mention, hair restoration surgeries provide permanent results!
Non-Invasive Hair Loss Treatments
If you don’t like invasive procedures, you can find other non-surgical alternatives that’ll help stimulate hair growth. Some of those treatments include PRP therapy, low-level lasers, and scalp micro-pigmentation.
It’s worth mentioning that the latter only gives the illusion of having short hair. However, it doesn’t stimulate hair growth.
Natural DHT Blockers
Now, don’t expect natural DHT blockers to provide similar results to minoxidil or finasteride. Those treatments may aid in hair loss treatment. However, relying on them solely most likely won’t produce satisfactory results.
Still, those ingredients might help slow hair loss. Some of the natural DHT blockers include:
- Pumpkin seed oil
- Caffeine
- Saw palmetto
- Rosemary oil
- Green tea
Ketoconazole
Ketoconazole is an antifungal drug used to treat various fungal and yeast infections. Aside from that, it can have antiandrogenic properties.
Similar to finasteride, ketoconazole shampoo can inhibit 5-alpha reductase, the enzyme that converts testosterone to DHT. Consequently, it might help reduce hair loss.
Conclusion
As you can see, minoxidil’s (Rogaine’s) sexual side effects are rare. While the former drug can cause adverse effects, they’re mostly related to skin issues.
Only a few cases reported experiencing sexual dysfunction problems when using minoxidil. However, further research is needed to support minoxidil’s possible sexual side effects.
Regardless of the adverse effects, you should consult with your dermatologist before using any form of minoxidil to determine whether or not this OTC treatment is suitable for you.