How to Restore Receding Temples With a Hair Transplant
Temple hair loss is one of the first signs of male pattern baldness. Around 50% of men over 50 years old experience some degree of hair loss in the temples. However, some men develop hair loss in their teens and early 20s.
If you’re experiencing receding temples, you might ask the question: how to restore receding temples with a hair transplant?
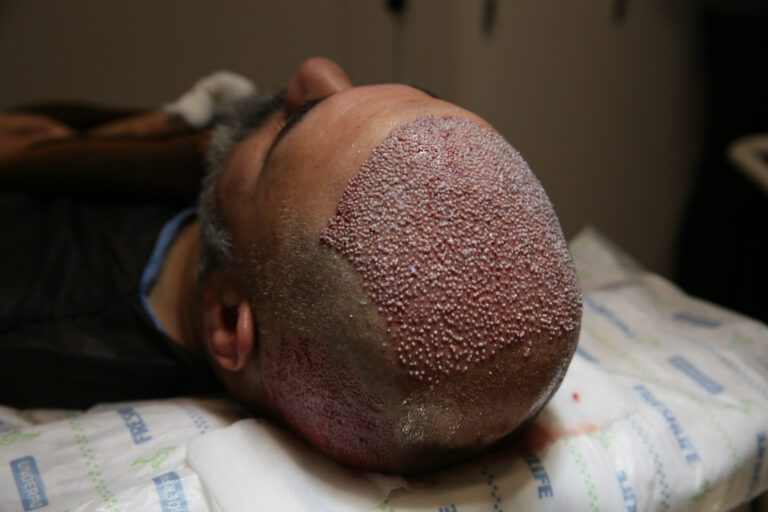
A Temple hair transplant is a surgical procedure where the surgeon removes hair from the back of the head (donor area) and implants it in the temple area. This technique helps temples to grow thick and dense hair.
If you’re experiencing hair loss or receding temples, don’t worry. In this article, we’ll discuss how to restore receding temples with a hair transplant.
What Are Balding Temples?
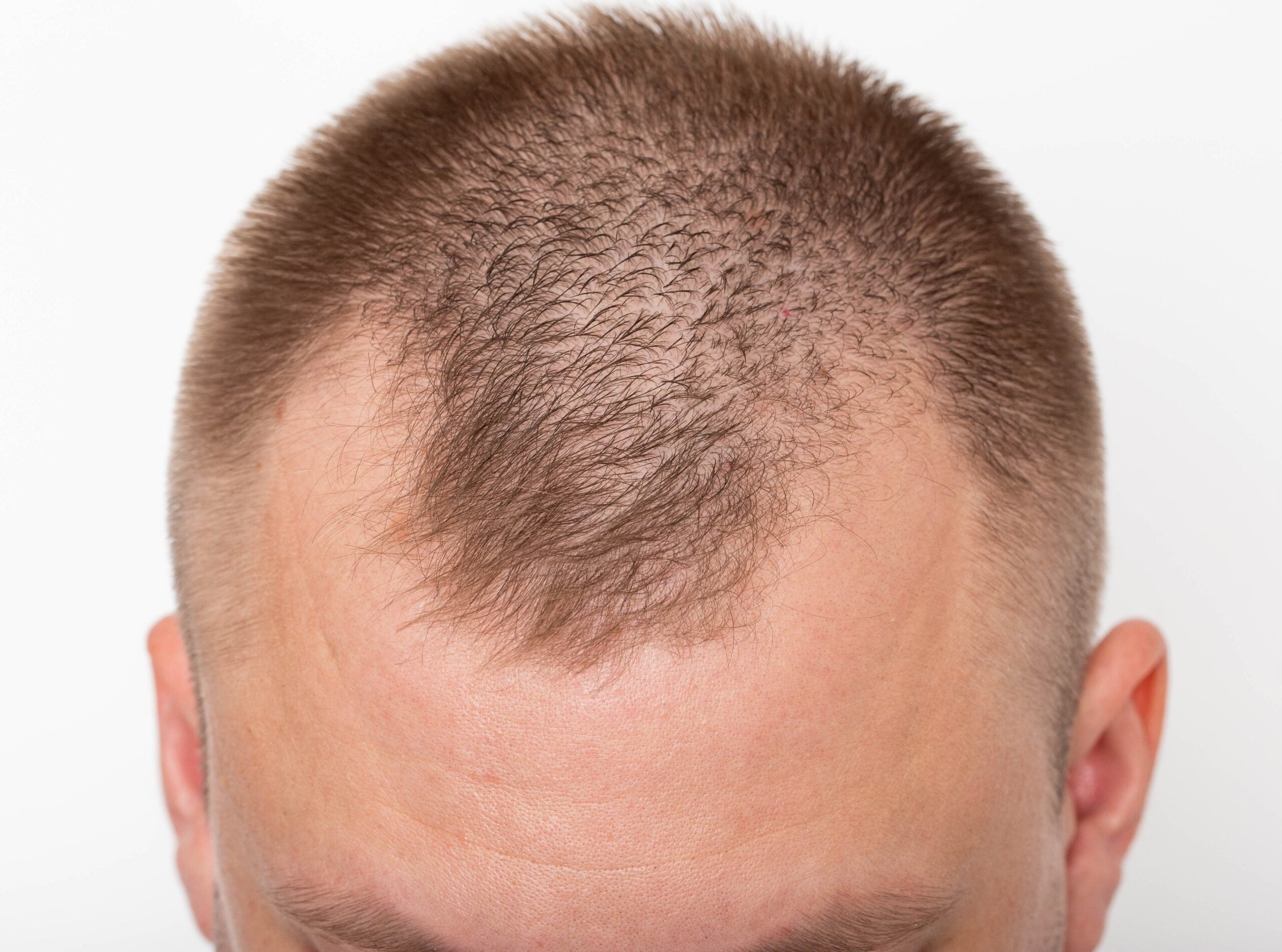
Temples are areas on your scalp between the eyes, cheekbones, ear, and forehead. Temple hair loss in males is also known as androgenic alopecia or male pattern baldness.
It’s a condition where hair starts to thin and recede in the temples. Hair receding can continue to the scalp, and in severe cases, it results in an M-shaped line.
Causes
Male pattern baldness is a genetic condition that usually starts with temple hair loss. The temples are one of the first places where hair loss can become noticeable.
The reason for this is that the temples are located in an area of the head that experiences a great deal of movement, which can put a lot of stress on the hair follicles. There are also other factors that contribute to temple hair loss in males.
- Smoking.
- Stress.
- Vitamin B deficiency.
- Traction alopecia.
- Hormonal changes.
- Medication side effects.
Researchers also found that male pattern baldness is linked to androgens. When androgens increase in the hair follicles, it shortens the cycle of hair growth, delays new hair growth, and produces thinner and shorter hair strands.
Treatment
Depending on the type and pattern of hair loss, your doctor will decide whether it can be treated with medication or a hair transplant.
Similar to most medical conditions, early diagnosis and intervention often attain better results. Your trichologist may recommend any of the following as a treatment for temple hair loss:
Minoxidil
Minoxidil is an FDA-approved topical treatment that provides temporary hair regrowth. It’s available as foam or solution and is usually prescribed to treat hair loss in men and women.
However, in most cases, it’s not effective as a lone treatment. It’s used in conjunction with other treatments.
Finasteride
Finasteride is another FDA-approved treatment for male pattern baldness. It decreases the levels of androgen by inhibiting the enzyme that converts testosterone into androgen.
The drug is often prescribed for men or women in menopausal age to treat genetic hair loss.
Hair Transplant for Temples
A hair transplant is often the best solution for temple hair loss if the above medications don’t work. The procedure is done by taking hair follicles from the back of the head and then implanting them in the areas with hair loss.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Treatment
PRP is a safe and noninvasive procedure for reducing hair loss in both males and females. It involves the extraction of platelets from the patient’s blood and using them to restore hair in bald areas.
Types of Hair Transplants for Temples
A hair transplant is one of the most effective procedures to reduce temple hair loss and other types of alopecia. The idea is to extract healthy hair follicles from one area in the scalp and implant them in bald areas to promote the growth of new dense hair.
There are two main types of temple hair transplants; FUT and FUE.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
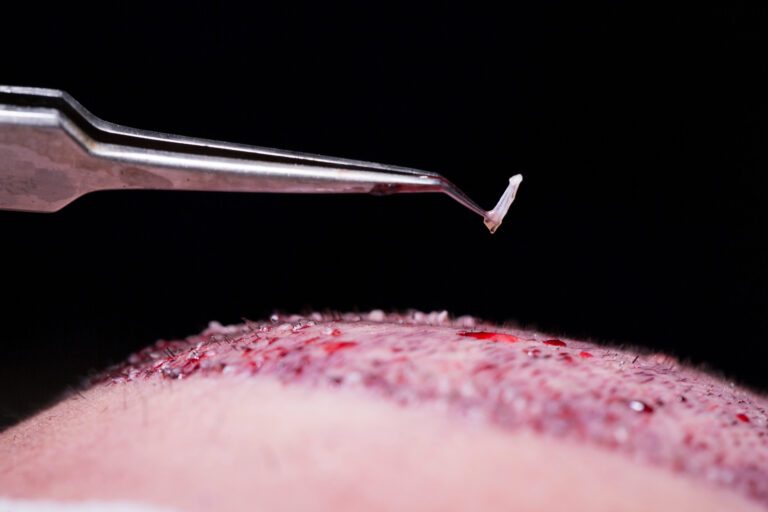
In this procedure, the surgeon removes a strip from the skin (usually the back of the head). Then, he uses a precision tool to extract hair follicles one by one. The removed strip is divided into grafts. Each graft contains one or a few hairs.
After that, the grafts are implanted into the bald area (recipient site). The wound is then closed and hidden using the surrounding hair.
The main downside of this technique is the scarring at the donor site. Some patients also experience pain and swelling in the area.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
Another popular procedure for hair transplant is FUE. The process involves shaving the back of the head and then extracting hair follicles, unlike FUSS, where an entire strip of scalp is removed.
After extracting hair follicles, the surgeon divides them into grafts. Then, he plants the grafts into the recipient site.
On the bright side, in this method, the donor sites heal very well, except for small dots which the surrounding hair can cover. In addition, since it’s less invasive than FUT, the patients are unlikely to experience post-operative pain and swelling in the donor area.
Moreover, hair follicle extraction involves taking hair follicles from several areas instead of a sole strip. That way, the hair thickness at donor sites remains the same.
The main downside of FUE is that it’s more expensive than FUT.
Recovery
It’s not uncommon to feel that your scalp is tender after FUT or FUE procedure. Your doctor will most likely prescribe antibiotics to prevent infection and some anti-inflammatory medications for pain and swelling.
Recovery time mainly depends on the type of surgical procedure. Patients who undergo FUSS usually take a longer time to recover.
However, you can expect to return to work after one day or a week at most. Within a few months, you should start noticing new hair growth on recipient areas as the hair grows around a half inch every month.
What’s the Difference Between Mature and Receding Hairline Temples?
People often confuse mature and receding hairlines. Even though they might look similar, they’re completely different.
Mature Hairline
A mature hairline is part of the aging process. It happens to all men starting at the age of 30 or the late 20s. The hairline starts to recede slightly along its original lines.
The receding could be more noticeable at the temples. That’s why many people think it’s a receding hairline.
In a mature hairline, the hair recedes by 1 cm to 2 cm. That said, it’s not a huge recession compared to a receding hairline.
Receding Hairline
On the other hand, receding hairline is not a natural process. It’s a type of hair loss where the hairline recedes unevenly, as some areas recede much faster than others.
The hairline retreats faster in the temple area, creating an M-shaped pattern known as a widow’s peak. Over time, the pattern becomes more severe until the whole hairline recedes.
The retreat in a receding hairline is usually a few centimeters, leading to a more exposed forehead. Furthermore, it can be followed by further hair loss and thinning at the crown, and in severe cases, people develop complete baldness.
Treatment
Since receding hairline is a hereditary condition, there are no medications that can completely stop hair loss. However, some treatments like Minoxidil and Finasteride can reduce a receding hairline.
Hair transplants are also effective in restoring hair loss during the receding process.
How to Prevent Temple Hair Loss
Unfortunately, genetic hair loss isn’t preventable. However, there are some tips you can follow to slow down the process of hair loss or thinning.
Stay Away From Damaging Hair Styles.
Hairstyles like cornrows, ponytails, and tight braids involve pulling hair away from the scalp. Even though the hair is flexible, it can only be stretched to some extent before being permanently damaged.
That’s why avoiding these hairstyles might slow down hair loss.
Eat a Healthy Diet
To keep your hair healthier and fuller, include many vitamins, omega-3s, and minerals in your diet. Avoiding refined sugar and processed food can also reduce hair loss.
Reduce Stress
Stress highly contributes to hair loss in men and women. Therefore, reducing stress levels has a positive impact on hair growth.
Participating in activities that reduce stress will help you in your battle against temple hair loss. From physical exercise to meditation and aroma therapy, there are a ton of ways to reduce stress.
Treat Underlying Medical Conditions
Even though temple hair loss is usually a genetic disorder, sometimes hereditary factors aren’t the only reason for hair loss.
Medical conditions such as thyroid disorder, syphilis, and hormonal imbalance cause hair loss. Treating these underlying medical conditions can help restore hair to its original growth rate.
Hair Regrowth Products
In some cases, hair regrowth products that contain Minoxidil or Finasteride come in handy to prevent further hair loss.
Depending on your type of hair loss, your doctor might prescribe these drugs to slow down hair loss.
To Wrap Up
Losing hair at the temples is an embarrassing and frustrating experience. However, it’s very common in males from the age of 30. Luckily, there are various treatments for this condition, from topical solutions and foams to hair transplants.
So answering the question: how to restore receding temples with a hair transplant? The process is similar to a normal hair transplant. The surgeon extracts hair follicles from a healthy part of the scalp. Then, he implants them into the bald areas in the temples to promote the growth of new thick, dense hair.