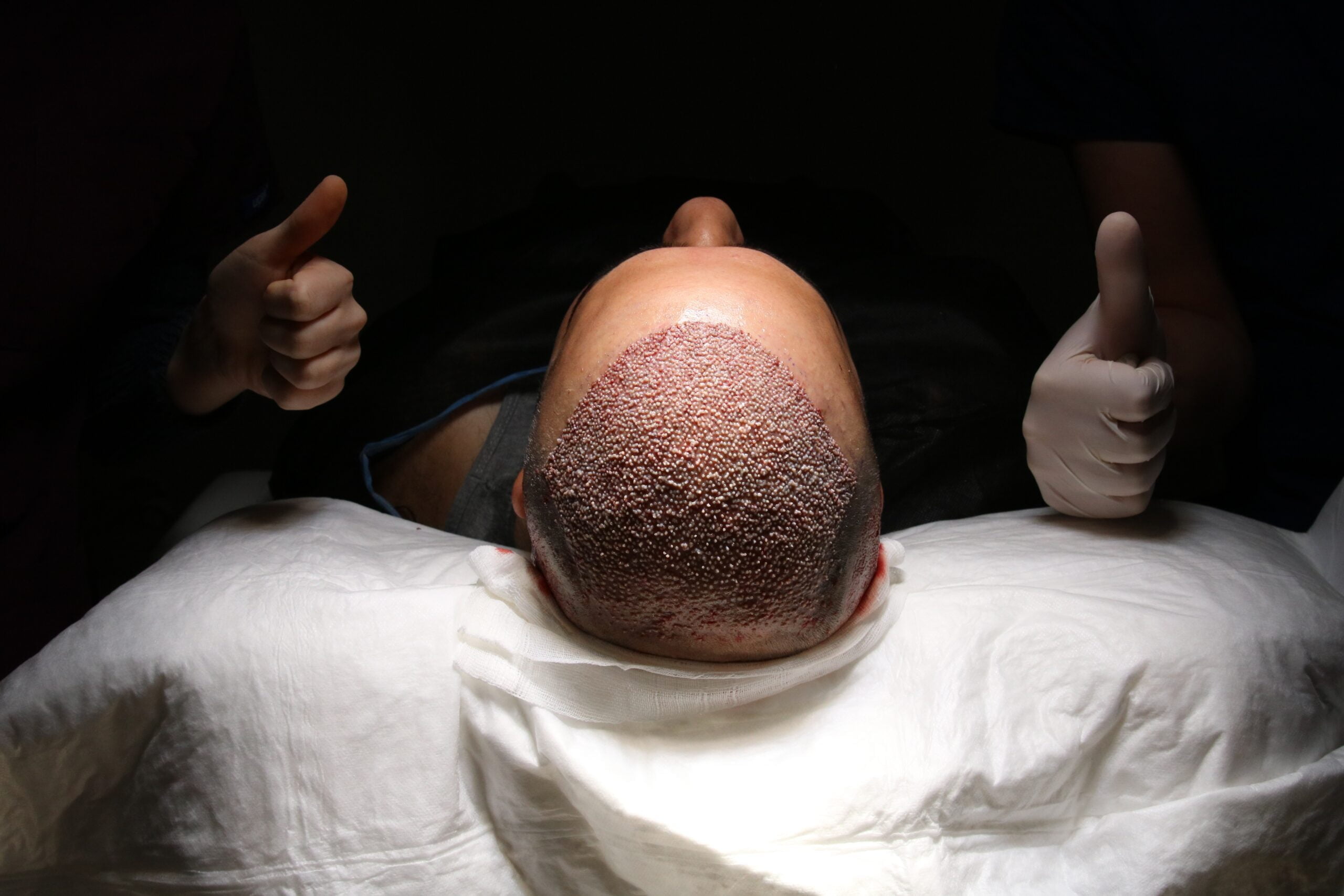
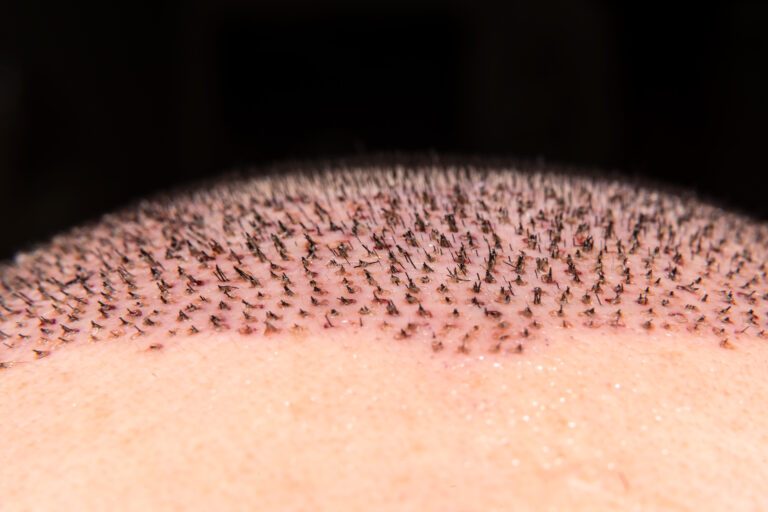
7 Side Effects To Expect When Getting Your Hair Transplant
When topical treatments prove ineffective, people turn to hair transplants to deal with baldness and thinning hair. Hair transplants can be life-changing, but they’re not without risks. Your doctor will give you a heads-up on these complications as part of the pre-surgery protocol.
Let’s look at the most common side effects of hair transplant, plus how to avoid and manage them.
1. Pain After Hair Transplant
The donor site receives more trauma during the transplantation, so it’s more susceptible to post-op pain.
You may experience mild FUE donor area pain after the surgery and once the local anesthesia has worn off. Taking over-the-counter pain meds usually helps, and many patients feel little to no pain for the rest of the week.
However, some may suddenly develop moderate to intense pain around the donor site. As the nerve endings awaken and the skin gets plump with fluid, pain and pressure build up around that area.
Patients describe their pain as:
- Sharp
- Stinging
- Burning
- Throbbing
- Tight
Inform your surgeon if you’re experiencing intense scalp pain along with other symptoms. You might have an infection that requires immediate medical attention.
Causes of Scalp Pain After Hair Transplant
It’s not uncommon for pain to persist for up to two weeks. Below are some causes of persistent scalp pain:
- An excessive number of harvested grafts
- Swelling, folliculitis, or infection
- Low tolerance to pain
- Delayed wound healing
That said, scalp pain can often be a natural part of the recovery process. As such, it’s nothing to worry about.
How to Manage Donor Area Pain
Here are some tips to ease normal post-op FUE donor area pain:
- Gently massage your scalp with vitamin E oil to release pressure from the area.
- Apply aloe vera gel to soothe your scalp.
- Take extra-strength pain meds.
- Avoid bending down or lifting heavy objects.
2. Swelling After Hair Transplant
Swelling or edema is a temporary side effect of hair transplants, especially among patients with grafts on their hairlines. People experience varying degrees of edema, so some may have it worse than others.
Most patients notice minor swelling on the forehead two days after the procedure. By days 3–4, the puffiness moves down to the temples and around the eyes. Then, the swelling disappears by the end of the week.
In rare cases, the areas around the eyes get so swollen that patients can’t open their eyes. Sometimes, bruises or discolorations appear on the eyelids.
Causes of Swelling
Swelling occurs after a hair transplant because of a fluid buildup. During the procedure, the anesthesiologist injects a tumescent solution (anesthetic diluted in saline) to make the tissues underneath the skin firm and tense.
The solution puffs up the skin by creating a space between the scalp and the skull. This technique reduces bleeding and aids in facilitating the extraction and insertion of follicular units.
How to Reduce Swelling After Hair Transplant
Apply these tips to minimize postoperative swelling:
- Limit your head movements for the first four days after the procedure.
- Sleep in a semi-upright position, with your head propped on a few pillows.
- Use a neck pillow for added support when sleeping.
- Apply an ice pack on swollen areas for 15 minutes every two hours.
- Avoid strenuous physical activities for the first two weeks after the hair transplant.
3. Hair Shedding After Hair Transplant
Hair goes through a three-phase cycle during development: growth, transition, and resting. Newly transplanted hair follicles might enter the resting stage after the shock of surgery.
Here are the stressful events during surgery that cause hair to shed:
- Cutting off blood supply to the hair grafts after extraction
- Anesthetics causing trauma to surrounding hairs
- Creation of recipient sites
Around weeks 2–4, hair from the newly transplanted grafts falls off. As a result, the hair around the recipient area may appear thinner.
There’s no need to worry, though; only the hair sheds—not the hair follicles. These structures that grow hair remain attached to the scalp.
New hair growth happens around three months after a period of adjustment and healing.
How to Reduce Shedding After Hair Transplant
Though shedding is unavoidable, you can take some steps to reduce it:
- Continue taking Propecia (Finasteride) to stabilize hair growth.
- Avoid using hair dyes and styling products.
- Stay out of the sun or use some protection when outdoors.
- Provide your hair with nutrients by eating a healthy diet.
4. Folliculitis and Infection
With Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), the surgeon extracts healthy hair follicles or grafts from an area of thick hair growth. A high-precision micro-punch tool is used during this process.
Afterward, the surgeon inserts the grafts from the donor site into the balding areas using a sharp implanter. Both extraction and grafting create open, dot-like wounds on your scalp.
Infections occur when microbes or pathogens get into the exposed skin around the donor or recipient sites. It can cause inflammation of hair follicles or folliculitis in medical terms.
Consult your doctor for a proper treatment plan if you suspect an infection.
Signs of Folliculitis
Watch out for these signs of folliculitis:
- Abscess or a pus-filled blister
- Redness or discoloration
- Pain
- Itchiness
- Tenderness and swelling
- Bleeding
Again, bleeding and inflammation are normal and should go away in a few days. However, symptoms that worsen or linger for more than a week are usual signs of infection.
Signs of Infection
Apart from folliculitis, you may also develop systemic (affecting the whole body) symptoms:
- Fever
- Headache
- Lethargy
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Nausea and vomiting
Causes of Folliculitis and Infection
The hair transplant team performs the procedure in a sterile environment to avoid contamination. Besides, the generous use of antiseptic keeps the wounds clean and germ-free during surgery.
However, you may still develop these complications because of the following reasons:
- Weak immune system or underlying medical conditions
- Unsanitary conditions and poor hygiene
- Excessive scabbing or itchiness that can lead to scratching
- Smoking
How to Avoid Folliculitis and Infection
Check out these tips for a smooth recovery after a hair transplant:
- Avoid intense physical activities for the first two weeks after the transplant.
- Do not wear a tight hat that can trap heat and moisture on your scalp.
- Follow the after-care instructions from the clinic.
- Avoid picking at your scabs or scratching your head.
- Change your pillowcases daily.
- Avoid smoking during recovery.
- Protect your scalp from dust, rain, or direct sunlight with loose headwear when outside.
5. Itching After Hair Transplant
Itchiness after a hair transplant is a good sign that your donor and recipient areas are healing. You’ll feel itchy during the first week when scabs form on your scalp.
New cells form, multiply, and close the wounds as they heal. They also release different chemical messengers to help make new tissues during this time.
One of these chemicals is histamine. It fires up the itch-sensing neurons as it prepares the body for an attack of foreign bodies in the healed areas.
Other Causes of Itching After Hair Transplant
Apart from scabbing, here are some reasons why you might feel the need to scratch post-surgery:
- Dirty scalp from not washing
- Allergic reaction to hair care products
- Infection
How to Stop Itching After Hair Transplant
Follow these tips to prevent your scalp from itching:
- Use a saline spray to remove dirt from your scalp during the no-wash days.
- Use a medicated shampoo when it’s time to wash your hair.
- Take antihistamine meds.
- Never scratch your itchy scalp to avoid infection, which can lead to more itching.
6. Scarring After Hair Transplant
Like other cosmetic procedures, a hair transplant requires finesse, precision, and expertise. Light scarring is unavoidable, but it’ll most likely be unnoticeable if a certified surgeon performs the procedure.
The amount of scarring is one reason patients prefer FUE. With this technique, scars appear as tiny dots on the donor site and are virtually undetectable in the recipient area. Even if you wear your hair short, people won’t be able to tell you’ve had a hair transplant.
With FUT, over-harvesting hair grafts from the donor site can leave a highly conspicuous linear scar. Of course, a good surgeon who cares about the patient will avoid this mistake.
How to Prevent Scarring After Hair Transplant
These are the ways to prevent postoperative scarring:
- Do your research and read patient reviews when looking for a hair transplant clinic.
- Make sure that a board-certified hair transplant surgeon is doing your procedure.
- Follow your surgeon’s aftercare instructions.
- Avoid harsh chemicals and heavily scented hair care formulas.
- Protect your scalp from damaging UV rays that can cause hyperpigmentation to your transplant scars.
7. Headache After Hair Transplant
It’s common to experience headaches after getting a hair transplant. You may feel tightness or swelling around the donor area, contributing to tension headaches. Anxiety and stress may also exacerbate your condition.
It’s best to follow up with your surgeon if you have an intense headache that doesn’t resolve with pain medication. If you have a fever, there’s a possibility you have an infection.
How to Prevent Headaches After Hair Transplant
Here are some tips to prevent post-surgery headaches:
- Do not smoke or consume alcohol during the first two weeks.
- Stay out of the sun’s intense heat.
- Keep yourself hydrated.
- Take paracetamol as needed.
- Relax and don’t overexert yourself.
Final Thoughts
All things considered, a hair transplant is a safe procedure you can get at a doctor’s office. It’s normal to experience some hair transplant side effects, but fortunately, they’re temporary.
Remember to maintain proper hygiene and follow aftercare instructions to ensure a smooth transition into recovery. Inform your surgeon if you have hair transplant side effects long term.